
 by Scott Jack
by Scott Jack
Content Contributor, E-N Computers
7+ years experience in healthcare IT and tech support.
When the Russian offensive on Ukraine began heating up in early 2022, there was concern that Russia would carry out more cyber attacks on U.S. organizations and critical infrastructure. Security experts and federal officials anticipated attacks from state-sponsored groups and cybercrime rings. In late January, the Department of Homeland Security warned of the threat.
Then in March, we talked with local news station WHSV about how this may affect small business and remote workers. We emphasized that the internet makes it possible for anyone to come right to our virtual doorstep. Because of this, every business needs to have strong security measures in place. Thankfully, U.S. organizations have not yet been severely impacted by Russian cyber attacks as a result of this conflict. However, intelligence officials are again warning businesses to be on high alert in the face of Russia’s renewed offensive against Ukraine.
On April 20, the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) issued a Cybersecurity Advisory warning of “increased malicious cyber activity” by Russian state-sponsored operations and affiliated cybercrime groups in response to unprecedented sanctions imposed on Russia and the material support the U.S. and its allies are providing in the conflict. While it is expected that attacks will primarily target critical infrastructure, it is also possible the software supply chain may be affected — a major example being the SolarWinds hack of 2020. The advisory recommends that all organizations immediately take practical steps to secure their computer systems, including user awareness training, software patching, and multi-factor authentication.
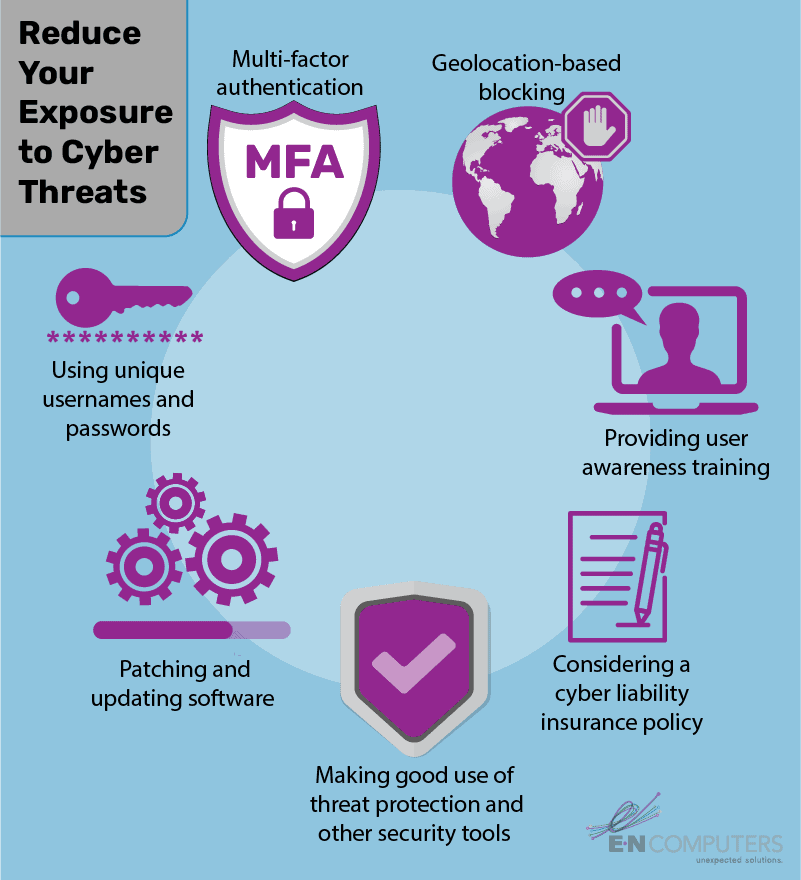
Today, we want to introduce seven practical steps, including those above, that you can take to reduce your exposure to cyber threats. In order, we’ll cover:
- Using unique usernames and passwords
- Enforcing multi-factor authentication
- Implementing geolocation-based blocking
- Providing user awareness training
- Patching and updating software
- Making good use of threat protection and other security tools
- Considering a cyber liability insurance policy
QUICK ANSWER:
How can I protect myself against cybercrime?
A combination of the right tools, the right processes, and the right awareness and training will help you and your organization to stay protected against cybercrime. A managed IT service provider can help you select the tools you need to stay secure.
Unique Usernames and Passwords 
A good place to start with improving security is to use unique usernames and passwords. Sensitive accounts, especially, should have unique usernames that are not easily guessed based on publicly available information. A common example in your personal life is that you don’t want the same username on your online banking profile that you use for social media or email.
Creating a unique password for every account can be a hassle. One way around this is to use a secure password management tool, like BitWarden or 1Password. These applications generate and store long, unique passwords for each of your accounts. They can also manage authentication codes for multi-factor authentication.
Multi-Factor Authentication 
Multi-factor authentication, sometimes abbreviated MFA or 2FA, builds on basic account security by requiring another factor, or proof, that you are allowed to log in. This is often described as using something that you know (your password) and something that you have — a mobile device or hardware token that provides an authentication code. MFA protects against login-based attacks and is available for many online services.
Geo-Blocking 
With geographic or location-based blocking, you specify a list of countries or regions that are not allowed to connect to your network. Alternately, you can create an allowlist that blocks traffic not coming from selected areas. Before your firewall accepts or creates a connection, it looks up the IP address in a database to verify its location before allowing it. Combined with MFA, geofencing provides an extra layer of security for your network.
However, many cybercriminals use VPNs or even other compromised systems inside of “friendly” countries to circumvent geo-blocking, so it’s not a perfect solution. Still, it can block many low-effort attacks that originate from countries known for cybercriminal activity and can keep users inside your network from connecting to malicious websites located in those countries. We implement geo-blocking by default on our Meraki firewalls and SD-WAN solutions, but most firewall vendors offer this capability.
User Awareness Training 
Though technical safeguards are important, they are not a replacement for good user behavior. Human error is a major factor in security incidents, so it’s important to provide your staff with training on good security practices and common threats. Often, hackers use social engineering to infiltrate a system before carrying out a more technically sophisticated attack.
A typical approach starts with a general phishing attack designed to trick staff into providing their credentials or other sensitive information. After gaining access, attackers will monitor your system to learn employee names, titles, modes of communication, and business processes, enabling them to mount a stronger and more targeted attack — directed at high-level staff (i.e. spear phishing) or mission-critical systems and data (e.g. DDoS or ransomware attacks).
User awareness training can happen online or in-person and covers a wide range of cybersecurity topics in a practical manner. Conducted on a regular basis, it can help minimize your risk. We offer customizable cybersecurity training and phishing simulations through our partner KnowBe4, which makes it easy to track who has been trained and who may need some additional reminders about cybersecurity.
Software Maintenance 
In addition to the user-facing practices we’ve covered so far, you also need to monitor and maintain your systems. One essential aspect of system maintenance is keeping your software — including the operating system and installed applications — updated. While updates sometimes introduce new features, they are most important because they fix bugs and security vulnerabilities on your system.
You should also know that many software providers, including Microsoft, place an end-of-life date on their products. For example, semi-annual releases of Windows 10 are retired after 18 months and Microsoft expects to fully retire Windows 10 in 2025 (official Windows 10 schedule). Machines with software past its end-of life will be vulnerable because the software will no longer receive security patches.
Threat Protection and Other Security Tools
It’s critical to monitor your systems for possible threats. The good news is you may already have the tools you need. Both Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace provide integrated threat protection tools that help catch malware, phishing, spam, and malicious links and attachments. We encourage our clients to make use of these tools since they can provide a deeper level of analysis and protection than a third-party tool.
If you have cyber liability insurance, which we’ll talk about next, we also encourage you to find out what tools your provider offers discounts for using. Modern cyber insurance providers offer managed detection and response to find and remediate threats early. Because the tool improves your security and provides the insurer with a better picture of your virtual environment, they can offer a customized, lower quote that best meets your needs.
Cyberinsurance 
Cyberinsurance is becoming more popular — and more expensive — due to a sharp rise in ransomware and other cyber attacks. Rates increased 20 to 50% in 2021 after seeing a substantial jump in the second half of 2020. Cyber insurance is a liability insurance product designed to handle expenses incurred from cyber attacks like business interruption costs, breach notifications, disaster recovery, legal expenses, and direct losses such as electronically stolen funds and ransom payments. It is usually separate from or in addition to a general liability policy.
We caution our clients to not rely too heavily on cyberinsurance, however. For one thing, it’s a reactive remedy; it only helps you after something has gone wrong. Proactive security is more effective at keeping you operational. Second, there are limits on what cyberinsurance policies will pay out (see this article for more details). Third and finally, current economic sanctions may limit the effectiveness of a cyberinsurance policy. Consider what could happen if your organization were hit by Russian ransomware.
Left unchecked, it would encrypt all your critical files. With no working backups, you would be left to start from scratch or pay a ransom. Normally, your insurer would help cover the cost of a ransomware payment so that your data could be decrypted. But because of sanctions, they may be unable or unwilling to make such a payment if it is believed to be going to a sanctioned country, including Russia.
Do you have a mature IT infrastructure in place that can maintain strong security while helping you meet your organizational goals? Take our short IT Maturity Evaluation to find out where you stand and get more actionable steps to improve your IT stance. You can also book a free strategy session to discuss your results with a member of our team.
Next Steps: Learn More About Incident Response
READ: How to Respond to a Cybersecurity Incident
READ: The Ultimate Guide to Backup and Disaster Recovery
To complement your security protocols, you should have an incident response plan (IRP) in place. An IRP identifies your security risks, your response team members, their roles, and the process they will use to evaluate, investigate, restore, and recover your systems after an attack. Read more on how to respond to a cybersecurity incident.
Your incident response plan will likely refer to your backup and disaster recovery (BDR) plan. The BDR identifies your systems and data: where they’re stored, how they are backed up, and how the backups can be used to restore data. Because the only thing worse than no backup is a bad backup, the BDR also outlines a process for testing backups regularly to verify that they work.
E-N Computers has helped dozens of companies to secure their systems, implement a backup and disaster recovery plan, and handle incident response. We can help you, too. Contact us today!
Take the IT Maturity Assessment

Is your business ready to weather changes, including employee turnover? Find out by taking our IT maturity assessment.
You’ll get personalized action items that you can use to make improvements right away. Plus, you’ll have the opportunity to book a FREE IT strategy session to get even more insights into your IT needs.

Industries
Locations
Waynesboro, VA
Corporate HQ
215 Fifth St.
Waynesboro, VA 22980
Sales: 540-217-6261
Service: 540-885-3129
Accounting: 540-217-6260
Fax: 703-935-2665
Washington D.C.
1126 11th ST. NW
Suite 603
Washington, DC 20001-4366
Sales: 202-888-2770
Service: 866-692-9082
VA DCJS # 11-6604
Locations
Harrisonburg, VA
45 Newman Ave.
Harrisonburg, VA 22801
Sales: 540-569-3465
Service: 866-692-9082
Richmond, VA
3026A W. Cary St.
Richmond, VA 23221
Sales: 804-729-8835
Service: 866-692-9082
